
Fix your full domain, computers, M365, and SaaS issues before your insurer jacks your costs
Know what they see
Don’t be one of the 14% of MSPs who lost clients after they missed what the hackers and insurance scans found.
Most MSPs focus on antivirus and firefighting vulnerabilities. Lavawall® differentiates your stack and focuses on holistic hygiene so you can relax and stand out and fill a gap that justifies premium pricing.
Internet
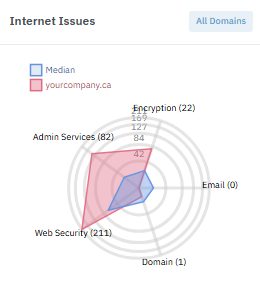
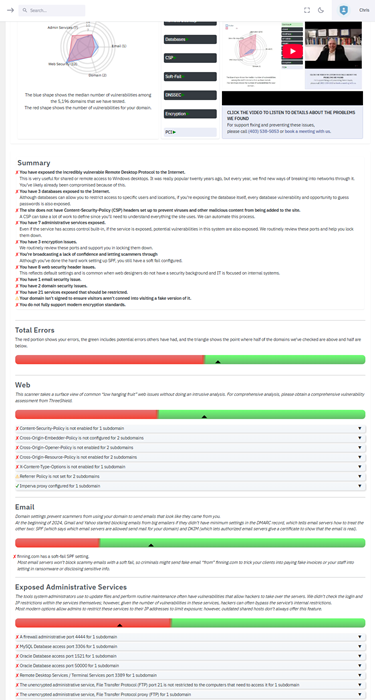
From transferrable domains and DMARC to outdated encryption and exposed admin tools on forgotten subdomains, Lavawall® even checks admin access to popular Content Management Systems, databases, and more!
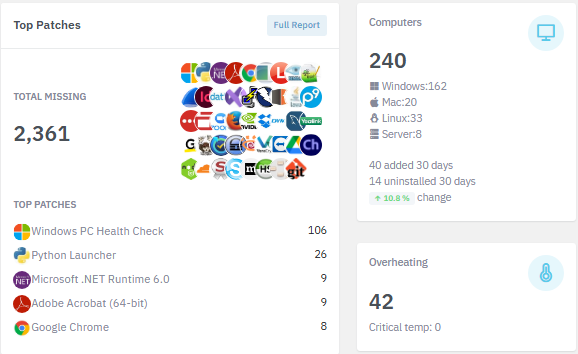
7,500+ Applications
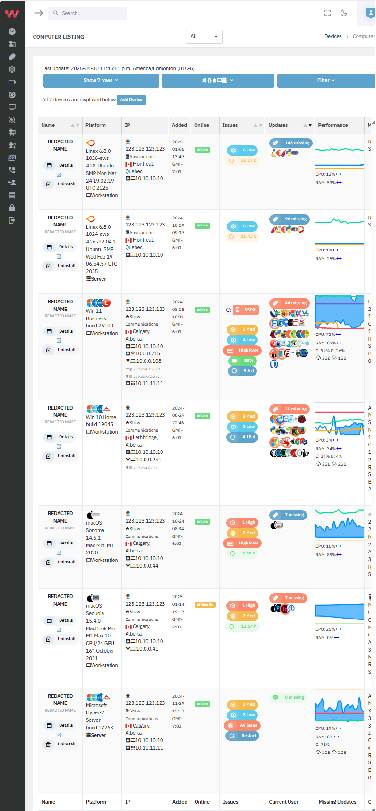
Reduce downtime and support tickets by proactively addressing 7,553+ risk-ranked Windows, Mac, and Linux applications plus Windows, Mac, and Linux OS & firmware updates.
View applications
Find your vulnerabilities
Quiet Revelation
Lavawall® scans are so quiet, you usually don't have to touch your firewall or WAF for them. The agents go deeper to find hidden settings the same way we audit governments and Fortune 50 companies.
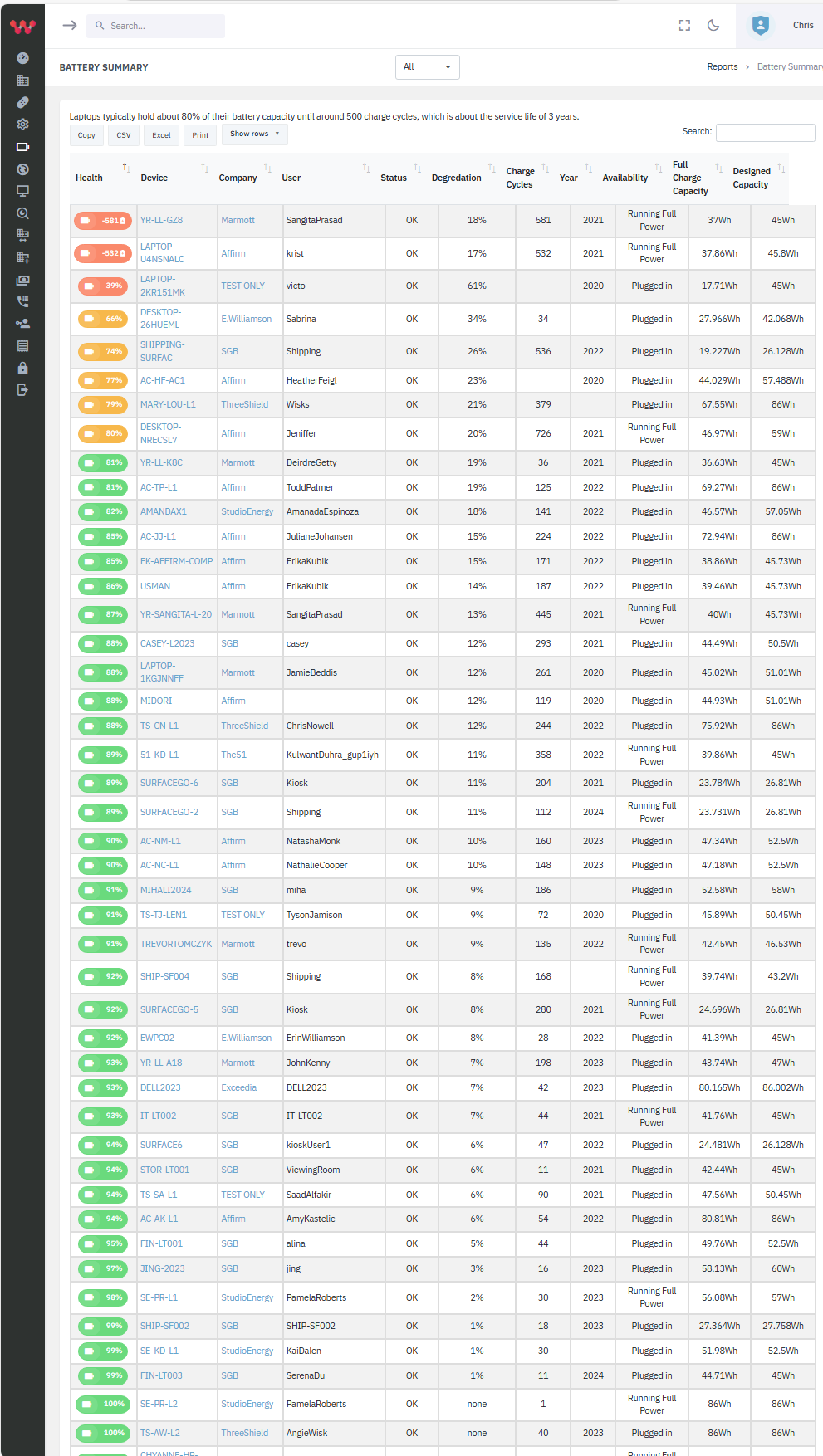
Then, amp up reliability with battery, temp, and other often-missed factors.
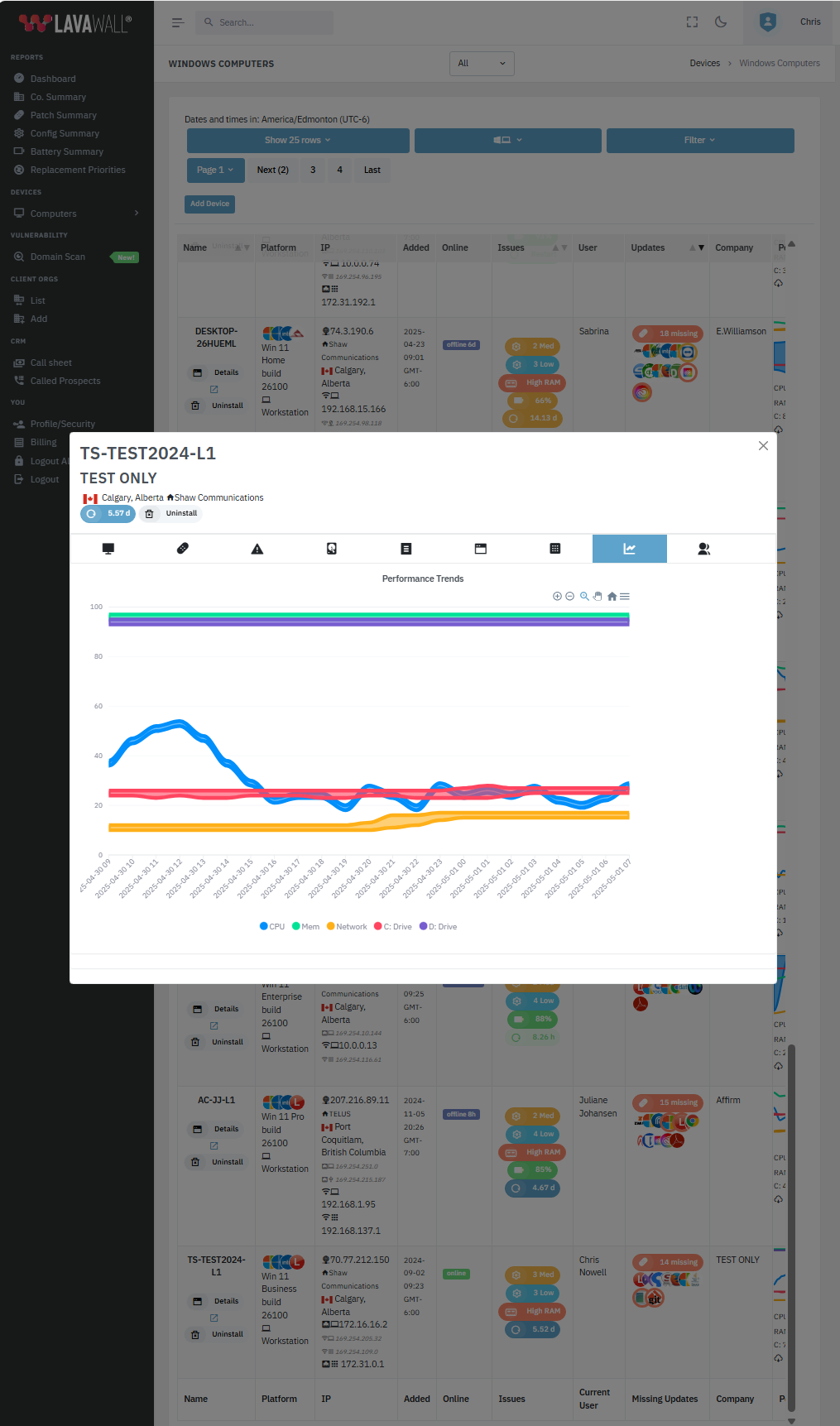
Easy Monitoring
From Huntress incidents, AV/MDR/XDR/EDR issues, and new domain/server issues to memory leaks and degraded batteries, get a quick view of problems before they blow up into critical incidents -- and then enable easy, ongoing monitoring.
Seriously: negative-cost cybersecurity
Save money and make money
Client discovery & optimization
- Build accurate, profitable quotes with fast, comprehensive client discovery.
- Keep your clients by securing applications and settings that your competitors miss.
- Reduce costs and increase productivity by finding problems with batteries, disks, and applications before users complain.
We don’t do long-term contracts, but we do decrease your costs as you grow, so your costs are optimized and you don't have to worry if a client shrinks. We'll never send you a new bill based on a bogus “high water mark” from months ago.
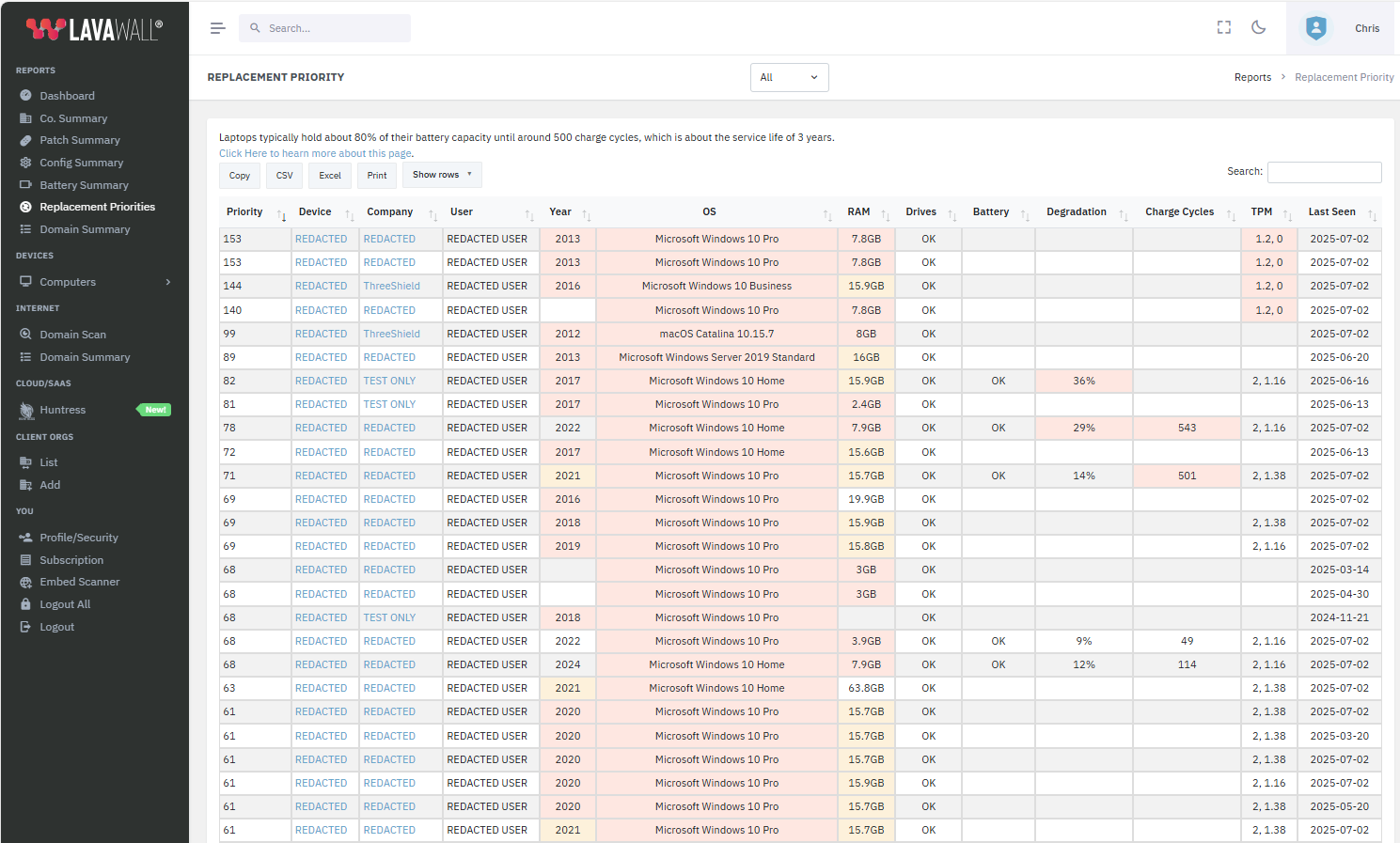
Client relationships with smart computer refresh
Deliver proactive upgrade recommendations that clients will actually act on.
Lavawall® helps you plan based with insights like degraded batteries, unreliable storage, maxed memory, or outdated TPM chips.
Increase reliability, justified sales, and satisfaction with optimized purchases driven by Lavawall’s simple, prioritized refresh lists.
Cyber insurance
Save yourself and your clients 10-20% on cyber insurance by finding Internet-exposed issues before your insurance assessor's scan does.
Not only does Lavawall® make you a rockstar to your clients and save them and you money, but it also gives you the evidence you need during a breach so you aren’t found liable.
White Label Security
Embed Lavawall® domain scanner results and printing functionality into your own website with custom phone and web call to actions to prove the need for cybersecurity to your MSP clients without requiring any admin access.
You can even use the tool to train your employees in cybersecurity and give about 87% of the value of a seasoned cybersecurity auditor.
Do you have questions?
Lavawall® is all about giving your users reliable computers, preventing hackers from getting in, and giving you confidence in arcane cybersecurity.
Here are the answers to some of the most common questions we hear.
If you have other questions, check out our FAQ page or call us in Calgary, Alberta at 1-403-538-5053; Vancouver, BC at 1-778-731-1339; or Mississauga, Ontario at 1-289-728-8829.
Seriously.
We were amazed that it worked too, but it is the easiest Mac security tool we’ve ever used.
We’re building more automated fix-it tools into Lavawall®, so it’s possible that if you ask us to help you, we might be able to give you early access to fix the problem yourself with one click.
If you’re working with one of our Managed IT Service Provider (MSP) partners, then we’ll direct you to them.
If you’re an MSP, we’ll happily help you directly or support your clients with our white label service.
If you aren't working with one of our partners, then we’ll gladly support you and quickly fix any issues that Lavawall® identifies.
We understand that this is a bit complicated. However, Lavawall® grew out of our MSP practice, where we endured vendors going around us to serve our clients directly so they could make a couple bucks and we don’t ever want to do that to our partners.
Take Lavawall® for a Spin
What would you like to do first? You can try either or both without a credit card.
If you decide to join, you can pay month-to-month without worries.